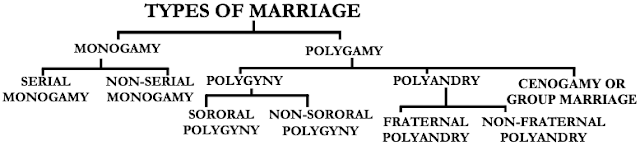
TYPES OR FORMS OF MARRIAGE:
As a universal social institution marriage is found to exist in all societies and at all stages of development. Types or forms of marriage vary from society to society but the institution of marriage is very much the same. In some societies, marriage is a religious sacrament whereas in others it is a social contract. However, there are several types of marriage that are classified on a different basis. This can be classified into three types as Monogamy, Polygamy and group marriage.
1. Monogamy:
Monogamy is an ideal, widespread and rational type of marriage. It is found in all civilized societies. Monogamy refers to a marriage in which one man marries one woman. Monogamy is of two types such as serial Monogamy and non-serial Monogamy.
i. Serial Monogamy:
In serial Monogamous marriage, the possibility of remarriage exists in case of divorce or death. Inspite of his remarriage, he remains to be monogamous.
ii. Non-serial Monogamy:
In the case of non-serial monogamy, the question of remarriage does not arise by either of the couples. Here a spouse has the same single-spouse throughout his life.
2. Polygamy:
Polygamy is a type of marriage in which there is a plurality of partners. It allows a man to marry more than one woman or a woman to marry more than one man at a time. Polygamy is of two types such as polygamy and polyandry.
a. Polygyny:
Polygyny is a type of marriage in which a man marries more than one wife at a time. It was practiced in most of the ancient civilizations. It prevailed among the ancient Hebrews, Assyrians, Babylonians, Indian and others. At present, it is widespread among primitive tribes but it is often simply confined to the wealthier classes. It is practiced among the Eskimo tribes, Crow Indians, African Negroes, the Naga, Gonds and Baigas of India. However, it is also permitted in Muslim Community. Polygyny is of two types:
i. Sororal Polygyny:
Sororal polygyny is often called a surrogate. The term surrogate comes from the Latin word ‘sorer’ which means sister. Accordingly, it refers to a marriage practice in which a man marries the sisters of his wife at a time or after the death of his wife.
ii. Non-Sororal Polygyny:
It is just opposite of the sororal polygyny, when a man marries several women at a time who are not necessarily sister to each other it is known as non-sororal polygyny.
b. Polyandry:
Polyandry is a very rare type of marriage in the present day. In this type of marriage, a woman marries several men at a time. In the words of K.M. Kapadia, “Polyandry is a form of union in which a woman has more than one husband at a time or in which brothers share a wife or wives in common”. It is practiced among the Tibetans, Marquesas Islanders of Polynesia, the Bahamas of Africa, the tribals of Samoa and others. In India, the tribes such as Tiyan, the Toda, the Kota, the Khasa and Ladakhi Bota also practice polyandry. The Nairs of Kerala were polyandrous previously. Polyandry is divided into two types:
i. Fraternal Polyandry:
When several brothers share a common wife it is called fraternal or adelphic polyandry. Draupadi’s marriage to Pandavas is a fine example of fraternal polyandry. The determination of the father is associated with some rituals. It is prevalent among the Todas.
ii. Non-fraternal Polyandry:
It is just the opposite of fraternal polyandry. In this type of marriage husbands of a woman is not necessarily brother to each other. This type of marriage is found among the Nairs of Kerala, Wife goes to spend some time with each of her husbands. So long as a woman lives with one of her husbands, the others have no claim on her. This mainly happens due to the scarcity of women.
3. Cenogamy or Group Marriage:
Group marriage means the marriage of two or more women with two or more men. Every woman is the wife of every man belonging to a particular group. Sociologists, like Dr. Rivers call it a kind of sexual communism. This type of marriage is found among some tribals in Australia, India, Tibet and Ceylon are believed to have practiced group marriage.


Post a Comment